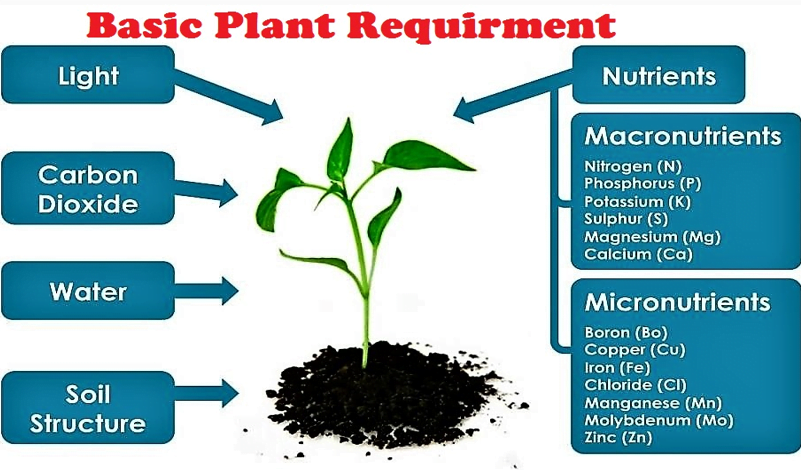
Soil
Soil Is a Living, Complex Ecosystem that Sustains plant, animals and human.
Soil Composition
Solid phase
Mineral constituents
Sand, Silt, Clay
Organic matter, both dead and
living micro and macro organisms
Liquid phase (Soil water )
Gas Phase (Soil air)
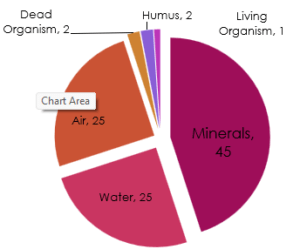
Soil Layers

Soil Health Character
Soil Quality and Health
Nutrient Function:- Chemical Fertility
Habitability Function:- Physical Fertility
Metabolic Function :- Biological Fertility
Chemical Character
Physical Character
Biological Character

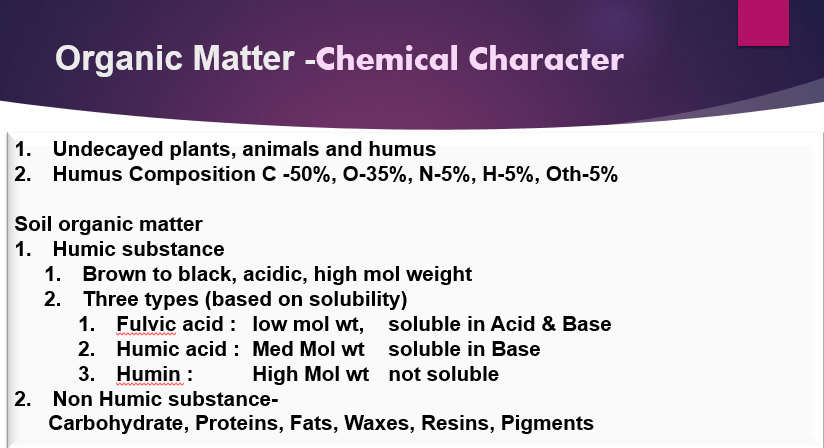

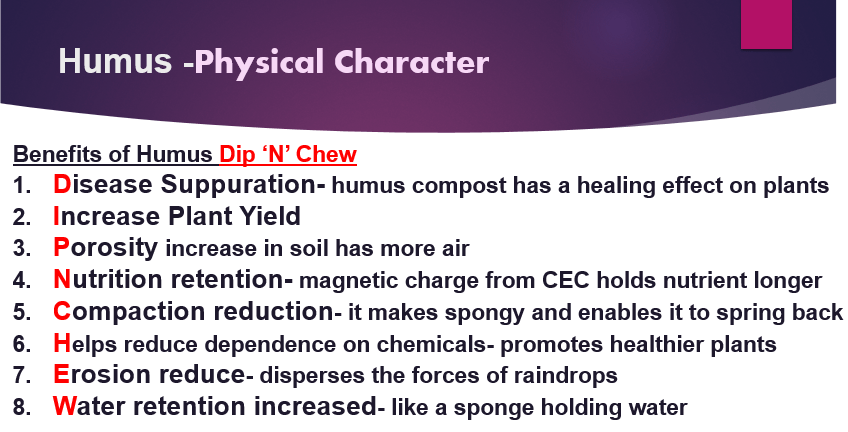

Humic Acid -Physical Character
1.Humic Acid maintains soil structure and enhances overall productivity
2.Improves soil structure and cation exchange capacity of soil.
3.Sustains and promotes beneficial soil microbial activity.
4.Acts as plant and root growth promoter and also as a seed germination stimulant.
5.Acts as buffer to control both excessive soil acidity and alkalinity.
6.Boosts fertilizer use efficiency.
7.Increases water holding capacity of soil and helps in water conservation.
8.Reduces contamination of water by preventing nitrate leaching.
9.Also increases soil aeration.
Finally, Acts as natural chelate to bind important minerals which would otherwise be unavailable to plants
Organic Carbon -Chemical Character
Total organic carbon influences many soil characteristics including
color, nutrient holding capacity (Cation and anion exchange capacity),
nutrient turnover and stability, water relations, aeration and workability.
Providing a food source for micro-organisms, help improve soil stability by micro-organisms binding soil particles together into aggregates. Bacteria excretions, root exudates, fungal hyphae and plant roots can all contribute to better soil structure
Moist, hot and well-aerated conditions favor rapid decay of organic additions.
Organic Carbon -Chemical Character
Plant nutrition: organic matter is a powerhouse of nutrients that are released into the soil.
Water retention: Organic matter has the capacity to absorb and retain water equivalent to up to 90% of its weight.
Soil structure aggregation: Organic matter results in clumping of the soil to form aggregates.
Prevention of soil erosion: It was found that an increase in soil organic matter from 1 to 3 % would result in lessening erosion up to 100-300%.
Microbes -Biological Character
1.Soil microorganisms are classified into seven different categories;
1.Bacteria,
2.Fungi,
3.Virus,
4.Blue-green algae,
5.Actinomycetes,
6.Protozoa, and
7.Nematodes.
2.The rhizosphere is a dynamic environment where plant roots release a variety of compounds that support higher microbial populations and activities than in bulk soil.
Bacteria -Biological Character
1.Bacteria are the smallest and most numerous cellular organisms in soils.
2.Bacterial biomass found in soil ranges from 108 to 109 bacteria in a gram of soil, most of them (>99%) have not been or cannot be cultured in the laboratory.
Common bacterial genera isolated from soil include Bacillus, Arthrobacter, Pseudomonas, Agrobacterium, Alcaligenes, Clostridium, Flavobacterium, Corynebacterium, Micrococcus, Xanthomonas, and Mycobacterium
Bacteria -Biological Character
1.Aerobic bacteria use oxygen as an electron acceptor; anaerobic bacteria use alternate electron acceptors such as nitrate, ferric iron, sulfate, carbonate, and organic matter.
2.Unlike the other soil microorganisms, most bacteria prefer nutrient-rich soils of neutral or slightly alkaline pH and a close C/N-ratio.
3.In contrast to simple morphology, bacteria have the greatest metabolic diversity.